The human body is an ideal environment for the habitat of pathogenic microorganisms, which can affect almost any organ or system, causing many diseases and disorders. Of these organisms, they have a special place for parasites that nourish and nourish the cells of the "owner" body and other nutrients. According to medical indicators, different age categories are approx. 90% of the carriers of parasites, which are treated and studied in the phase of medicine - parasitology. The term "parasites" means that various types of living organisms that are capable of settling in the human body, introduced in the tissues of the internal organs, consume cells, fruit juices or digested foods. Foreign organisms can penetrate any part of our body and live in a man's life for a long time. Some parasites of the human body do not cause special changes, but there are some that can negatively affect the "farmer" well and cause some serious illnesses. In such cases, we are talking about parasitic diseases that require immediate treatment. In medicine, parasites are called any pathogenic organism that leads a parasitic lifestyle in the human body. These include various bacteria, viruses, fungi, and worms, simple, single -celled, arthropods, protozoal invasions and other species.
What are parasitic diseases?
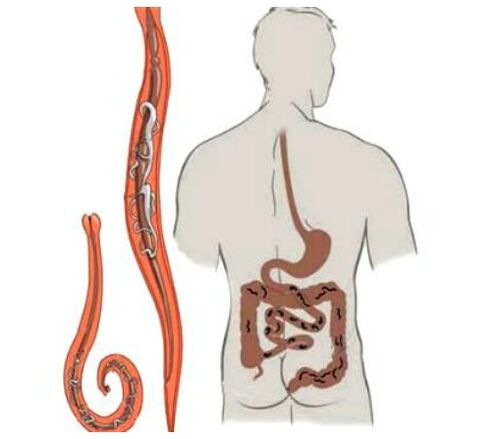
Parasitic diseases (invasions) are a large group of diseases caused by various pathogenic organisms that live and reproduce inside a person. There are about 300 types of parasites that can affect the human body. Parasitic diseases can be caused by both pathogenic bacteria and parasitic protozoa, arthropods, unicellular and other parasites or viruses. The list of parasites of the human body is quite large, but regardless of the type, almost every toxin that destroys cell structures, damages the internal organs, penetrates the lymphatic stream, blood that poisons the body and disrupts the work of internal organs and systems.
Basically, pathogenic organisms consume nutrients that a person gets with food. The behavior of the "unexpected guests" may explain that many people who lead the right lifestyle monitor their health and foods do not get the desired result, as these "Darmists" lose all good, so that only a small particle remains from the useful materials. These creatures are so cunning that they are often disguised as other diseases and a person can have been around doctors for years, but does not notice the positive result of treatment.
How do the parasites fall into the human body?
Foreign organisms can penetrate the human body in several ways, but the infection is most often:
- Water or soil infected with worms.
- Food products that have not yet handed over the desired processing: poor meat, fish, dirty vegetables, fruits, dairy products.
- Contact with household or homeless animals.
- Insect bites.
- To satisfy personal hygiene rules.
- Close the connection with the carrier carrier.
Many parasites in the human body have no nervous, cardiovascular or respiratory system, but their reproductive organs can throw hundreds of thousands of mature eggs into the environment. The eggs and larvae of the parasites are very stable and can be in the soil, water, food or personal objects for a long time. For example, tapeworm eggs can withstand minus 15 degrees and can maintain their vital activity for 9 months. Almost every parasite has a protective mechanisms that cannot recognize and destroy the human body. Therefore, it is difficult to diagnose many parasitic diseases. Pathogenic organisms can be both in the intestine, the lungs, the blood, the liver, the joints, the brain and even in the eyes. The location of the localization of pathogenic organisms depends on its type and other qualities, both man and parasite.
Parasites in the body distinguish between substances that live in one person for many years. They do not have a digestive system, but the parasites only use the beneficial materials that enter the human body that allow them to live for years, while one slowly loses their health and does not suspect the real cause.
Special organisms use their "tools" for adapting to new conditions: pointed hooks, plates, hard hairs, and suction courses that are constantly injured in the organ membranes of the organs. Parasites themselves can be several millimeters long for several meters, and are capable of secreting various toxins that poison the body as a whole and not only causes disorders in the work of the internal organs, but also suppresses immunity, destroys the beneficial bacteria of the stomach tract and overloads the liver.
Signs and symptoms of parasites in the body

Parasites in the body - the symptoms of their presence may lack or resemble clinical manifestations of other diseases. For example, the larvae in the lungs cause symptoms of pneumonia, pinworms symptoms - appendicitis and parasites - barrels of gallbladder or pancreatitis.
In addition, parasitic diseases are capable of frequent colds, sore throat, bronchitis and other diseases. You may suspect that the presence of parasites in the human body is as follows:
- Disorders in the work of the stomach system: diarrhea, bloating, frequent constipation, irritable bowel syndrome
- Joint and muscle pain
- Allergic skin reactions
- Anemia: A lot of "coexisters" feed on blood that leads to an iron deficiency anemia
- Reduce or increase body weight
- Violation of the work of the psyche. Toxins distinguishing parasites have a devastating effect on the nervous system, which causes a person's increased irritability, nervousness, frequent depression, panic attacks and other disorders,
- Brooksism - teeth in a dream
- Intestine
- Violation of the work of the immune system. Many worms and parasites reduce the production of immunoglobulin, which over time leads to a reduction in immunity. Man is completely defenseless before viral and infectious diseases
- Respiratory inflammatory processes
- Oncological diseases. The long -term detection of a parasite in the body causes a significant decrease in immunity and cancer degeneration of epithelial cells
In addition to the above symptoms, parasitic invasions often damage the liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system, leading to violation of their work and many diseases that are difficult to treat. It is important to note that all the above signs of parasites in the human body do not accurately confirm their presence. Only professional and high -quality diagnostics help to determine the presence or absence of "non -called guests".
How to recognize the parasitic disease
It is quite difficult to diagnose the presence of helmink, especially after infection. Until recently, the only way to identify "strangers" is the analysis of duodenal sound and stool analysis. The results of such studies allowed the determination of fragments, larvae or eggs of parasites. However, such methods did not always give reliable results. Currently, modern techniques are used to detect parasites that allow almost all parasites.
- Calais analysis (done at least three times)
- Immunoform analysis (Elisa)
- Elisa tests
- Serological research methods
- Ultrasound examination of internal organs (ultrasound)
- Computer tomography
- PCR diagnostics offers analysis of parasites based on DNA analysis
Research results allow not only the presence of parasites in the body, but also to evaluate the condition of the internal organs and to identify other diseases or disorders.
Treatment of parasitic diseases
Treatment of parasitic diseases depends on many factors: a specific type, size, quantity, patient's age, body weight and other properties. In the pharmaceutical industry, a large selection of drugs against parasites is offered, but not all drugs can overcome a particular parasite. It is important to note that almost all parasites violate the work of the internal organs, so the patient should be prescribed a comprehensive treatment, which is not only aimed at destroying the invasion, but also to restore the damaged internal body.
In addition to synthetic drugs, antibiotics anti -worms, antiparasitic agents containing natural components are used in the treatment of parasites. Such funds have no contraindications and are well tolerated by the human body.
Only the doctor should treat parasitic diseases after the results of the research and the determination of the pathogenic body. The names of the treatment, doses and drugs are prescribed separately for each patient. All antiparasitic drugs have many contraindications and side effects, so they need a doctor consultation before they use.
It is important to use drugs in the treatment of parasites that restore the functionality of the stomach, liver and kidneys, promote immunity, and provide the body with vitamin preparations. Not less than the most important thing in treating parasitic diseases, it is considered a proper nutrition. Patients should exclude the diet of meat and dairy products as they are ideal for the spread of parasites. The use of sugar and sweets should also be completely excluded. Nutrition should be balanced, high quality and useful for the body.
The prognosis after the treatment of parasitic diseases is basically favorable, but in the case of large -scale large parasites or significant damage to the internal organs arranged in the body, it is difficult to predict the result after treatment.
Preventing parasitic diseases

You can protect yourself from penetrating parasites, but only if you follow the simple rules. Prevention of parasites lies in a man's body:
- To follow personal hygiene rules
- Lack of contact with homeless animals
- Avoid children near pets
- Play with a child on the street to make sure not to answer different objects
- After playing in the sandbox, be sure to wash your hands
- Do not eat on the street during walks, only after washing their hands
- Regular cleaning of the house
- Use only washed and treated vegetables, fruits
- Eat only well festar meat
- Drink only cooked water
- If any animal needs the whole family in the house, once every 6 months to prevent parasitic diseases.
Compliance with simple preventive rules allows for protection against infection with parasites, thereby protecting yourself and your family from possible disorders of the work of internal organs, which often show the background of parasitic diseases.